Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
At the heart of all ERP systems is a database, when a user enters or updates information in one module, it is immediately and automatically updated throughout the entire system

ERP systems automate business processes

Bringing the Organization Together
ERP – The organization before ERP

ERP – bringing the organization together

The Evolution of ERP

Integrating SCM, CRM, and ERP
1)SCM, CRM, and ERP are the backbone of e-business
2)Integration of these applications is the key to success for many companies
3)Integration allows the unlocking of information to make it available to any user, anywhere, anytime
SCM and CRM market overviews


General audience and purpose of SCM, CRM and ERP

Integration Tools
Many companies purchase modules from an ERP vendor, an SCM vendor, and a CRM vendor and must integrate the different modules together
1)Middleware – several different types of software which sit in the middle of and provide connectivity between two or more software applications
2)Enterprise application integration (EAI) middleware – packages together commonly used functionality which reduced the time necessary to develop solutions that integrate applications from multiple vendors
Integration Tools
Data points where SCM, CRM, and ERP integrate

Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
ERP systems must integrate various organization processes and be:
1)Flexible- must be able to quickly respond to the changing needs of the organization
2)Modular and open-must have an open system architecture, meaning that any module can be interface, with or detached whenever required without affecting the other modules.
3)Comprehensive- must be able to support a variety of organizational functions for a wide range of businesses
4)Beyond the company- must support external partnerships and collaboration efforts
Enterprise Resource Planning’s Explosive Growth:
SAP boasts 20,000 installations and 10 million users worldwide
ERP solutions are growing because:
-ERP is a logical solution to the mess of incompatible applications that had sprung up in most businesses
-ERP addresses the need for global information sharing and reporting
-ERP is used to avoid the pain and expense of fixing legacy systems
Tuesday, 18 February 2014
Chapter 12 :Integrating the Organization from End to End – Enterprise Resource Planning
Posted by Unknown at 19:55 0 comments
Tuesday, 11 February 2014
Chapter 11 : Building a Customer-Centric Organization – Customer Relationship Management
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) :
CRM enables an organization to:
1)Provide better customer service
2)Make call centers more efficient
3)Cross sell products more effectively
4)Help sales staff close deals faster
5)Simplify marketing and sales processes
6)Discover new customers
7)Increase customer revenues
Recency, Frequency, and Monetary Value :
Organizations can find their most valuable customers through “RFM” - Recency, Frequency, and Monetary value
How recently a customer purchased items (Recency)
How frequently a customer purchased items (Frequency)
How much a customer spends on each purchase (Monetary Value)
The Evolution of CRM:
CRM reporting technology – help organizations identify their customers across other applications
CRM analysis technologies – help organization segment their customers into categories such as best and worst customers
CRM predicting technologies – help organizations make predictions regarding customer behavior such as which customers are at risk of leaving
Three phases in the evolution of CRM include reporting, analyzing, and predicting


The Ugly Side of CRM

Customer Relationship Management’s Explosive Growth
CRM Business Drivers

Customer Relationship Management’s Explosive Growth
Forecasts for CRM Spending (in billions)

Using Analytical CRM to Enhance Decisions
Operational CRM – supports traditional transactional processing for day-to-day front-office operations or systems that deal directly with the customers
Analytical CRM – supports back-office operations and strategic analysis and includes all systems that do not deal directly with the customers
The primary difference between the two is the direct interaction between the organization and its customer.
Operational CRM and analytical CRM

Customer Relationship Management Success Factors :
CRM success factors include:
1)Clearly communicate the CRM strategy
2)Define information needs and flows
3)Build an integrated view of the customer
4)Implement in iterations
5)Scalability for organizational growth
Posted by Unknown at 00:44 0 comments
Chapter 10 : Extending the Organization – Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management :
1) The average company spends nearly half of every dollar that it earns on production
2) In the past, companies focused primarily on manufacturing and quality improvements to influence their supply chains
Basics of Supply Chain :
The supply chain has three main links:
1)Materials flow from suppliers and their “upstream” suppliers at all levels
2)Transformation of materials into semifinished and finished products through the organization’s own production process
3)Distribution of products to customers and their “downstream” customers at all levels
Organizations must embrace technologies that can effectively manage supply chains


PLAN
1)Aim:plan for managing all the resources that go toward meeting customer demand for products or services.
2)Activity: develope a set of metrics to monitor the supply chain so that it is efficient, costs less, and delivers high quality and value to customers.
SOURCE
Aims:
choose reliable suppliers that will deliver goods and services required for making products.
develop a set of pricing, delivery, and payment processes with suppliers and create metrics for monitoring and improving the relationships.
MAKE
Activity: include scheduling the activities necessary for production, testing, packaging, and preparing for delivery.
DELIVER
commonly referred to as logistics.
Logistics is the set of processes that plans for and controls the efficient and effective transportation and storage of supplies from suppliers to customers.
Activity: companies must be able to receive orders from customers, fulfill the orders via a network of warehouses, pick transportation companies to deliver the products, and implement a billing and invoicing system to facilitate payments.
RETURN
Activity: create a network for receiving defective and excess products and support customers who have problems with delivered products.
Information Technology’s Role in the Supply Chain:
IT’s primary role is to create integrations or tight process and information linkages between functions within a firm


Visibility
1)Supply chain visibility – the ability to view all areas up and down the supply chain
2)Bullwhip effect – occurs when distorted product demand information passes from one entity to the next throughout the supply chain
Consumer Behavior
1)Companies can respond faster and more effectively to consumer demands through supply chain enhances
2)Demand planning software – generates demand forecasts using statistical tools and forecasting techniques
Competition
1)Supply chain planning (SCP) software– uses advanced mathematical algorithms to improve the flow and efficiency of the supply chain
2)Supply chain execution (SCE) software – automates the different steps and stages of the supply chain
SCP and SCE in the supply chain

Speed
Three factors fostering speed

Supply Chain Management Success Factors

Supply Chain Management Success Factors
SCM industry best practices include:
1)Make the sale to suppliers
2)Wean employees off traditional business practices
3)Ensure the SCM system supports the organizational goals
4)Deploy in incremental phases and measure and communicate success
5)Be future oriented
SCM Success Stories
Top reasons why more and more executives are turning to SCM to manage their extended enterprises

Numerous decision support systems (DSSs) are being built to assist decision makers in the design and operation of integrated supply chains
DSSs allow managers to examine performance and relationships over the supply chain and among:
1)Suppliers
2)Manufacturers
3)Distributors
4)Other factors that optimize supply chain performance

Posted by Unknown at 00:34 0 comments
Sunday, 9 February 2014
Chapter 9 : Enabling the Organization Decision Making
Decision-enabling, problem-solving, and opportunity-seizing systems

The reasons for the growth of decision-making information systems :
1)People need to analyze large amounts of information
2)People must make decisions quickly
3)People must apply sophisticated analysis techniques, such as modeling and forecasting, to make good decisions
4)People must protect the corporate asset of organizational information
DECISION MAKING
Model – a simplified representation or abstraction of reality
IT systems in an enterprise

Transaction Processing Systems
Moving up through the organizational pyramid users move from requiring transactional information to analytical information

1) Transaction processing system : the basic business system that serves the operational level (analysts) in an organization
2) Online transaction processing (OLTP): the capturing of transaction and event information using technology to (1) process the information according to defined business rules, (2) store the information, (3) update existing information to reflect the new information
3) Online analytical processing (OLAP : The manipulation of information to create business intelligence in support of strategic decision making
Example of TPS
Types of TPS are used at your college:
Payroll system (Tracking hourly employees)
Accounts Payable system
Accounts Receivable system
Course registration system
Human resources systems (tracking vacation, sick days)
Decision Support Systems :
Decision support system (DSS) – models information to support managers and business professionals during the decision-making process
Three quantitative models used by DSSs include:
Sensitivity analysis – the study of the impact that changes in one (or more) parts of the model have on other parts of the model
What-if analysis – checks the impact of a change in an assumption on the proposed solution
Goal-seeking analysis – finds the inputs necessary to achieve a goal such as a desired level of output
What-if analysis

Goal-seeking analysis

Decision Support Systems
Interaction between a TPS and a DSS

Executive Information Systems:
Executive information system (EIS) – a specialized DSS that supports senior level executives within the organization
Most EISs offering the following capabilities:
Consolidation – involves the aggregation of information and features simple roll-ups to complex groupings of interrelated information
Drill-down – enables users to get details, and details of details, of information
Slice-and-dice – looks at information from different perspectives
Interaction between a TPS and an EIS

Digital dashboard – integrates information from multiple components and presents it in a unified display


Artificial Intelligence (AI):
Intelligent system :various commercial applications of artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI): simulates human intelligence such as the ability to reason and learn
Four most common categories of AI :

1)Expert system – computerized advisory programs that imitate the reasoning processes of experts in solving difficult problems
2)Neural Network – attempts to emulate the way the human brain works
3)Fuzzy logic – a mathematical method of handling imprecise or subjective information
4)Genetic algorithm – an artificial intelligent system that mimics the evolutionary, survival-of-the-fittest process to generate increasingly better solutions to a problem
5)Intelligent agent – special-purposed knowledge-based information system that accomplishes specific tasks on behalf of its users
6)Multi-agent systems
7)Agent-based modeling
DATA MINING
Data-mining software includes many forms of AI such as neural networks and expert systems

Common forms of data-mining analysis capabilities include:
-Cluster analysis
-Association detection
-Statistical analysis
Cluster Analysis

Association Detection

Statistical Analysis

Posted by Unknown at 20:49 0 comments
Wednesday, 5 February 2014
Chapter 8 : Accessing Organizational Information-Data warehouse
DATA WAREHOUSE.
History of data warehousing :
In the 1990’s executives became less concerned with the day-to-day business operations and more concerned with overall business functions.
The data warehouse provided the ability to support decision making without disrupting the day-to-day operations, because:
Operational information is mainly current,does not include the history for better decision making,Issue of quality information.Without information history, it is difficult to tell how and why things change over time.
DATA WAREHOUSE FUNDAMENTALS
Data warehouse is a logical collection of information which gathered from many different operational databases that suppports business analysis activities and decision-making tasks.
The primary purpose of a data warehouse is to combined information throughout an organization into a single repository for decision-making purposes.Data warehouse support only analytical processing.
DATA WAREHOUSE MODEL
1)Extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) – a process that extracts information from internal and external databases, transforms the information using a common set of enterprise definitions, and loads the information into a data warehouse.
2)Data warehouse then send subsets of the information to data mart.
3)Data mart – contains a subset of data warehouse information

~Multidimensional Analysis and Data Mining~
1) Relational Database contain information in a series of two-dimensional tables.

In a data warehouse and data mart, information is multidimensional, it contains layers of columns and rows
Dimension is a particular attribute of information.

2) Cube is common term for the representation of multidimensional information.

i. Once a cube of information is created, users can begin to slice and dice the cube to drill down into the information.
ii.Users can analyze information in a number of different ways and with number of different dimensions.
Data mining is the process of analyzing data to extract information not offered by the raw data alone. Also known as "knowledge discovery" – computer-assisted tools and techniques for sifting through and analyzing vast data stores in order to find trends, patterns, and correlations that can guide decision making and increase understanding.
To perform data mining users need data-mining tools:
Data-mining tool – uses a variety of techniques to find patterns and relationships in large volumes of information. Eg: retailers can use knowledge of these patterns to improve the placement of items in the layout of a mail-order catalog page or Web page.
INFORMATION CLEANSING OR SCRUBBING
An organization must maintain high-quality data in the data warehouse
Information cleansing or scrubbing – a process that weeds out and fixes or discards inconsistent, incorrect, or incomplete information
Occur during ETL process and second on the information once if is in the data warehouse
1) Contact information in an operational system
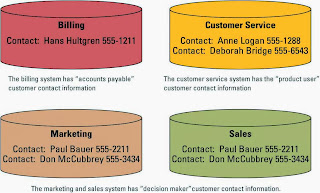
2) Standardizing Customer name from Operational Systems

3) Information cleansing activities

4) Accurate and complete information


BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE
Business intelligence is refers to applications and technologies that are used to gather, provide access, analyze data, and information to support decision making effort.these systems will illustrate business intelligence in the areas of customer profiling, customer support, market research, market segmentation, product profitability, statistical analysis, and inventory and distribution analysis to name a few.Eg: Excel, Access
Posted by Unknown at 19:16 0 comments
Tuesday, 4 February 2014
Chapter 7 : Storing Organizational Information
What is information?
Information is everywhere in an organization.
Information is stored in databases
Database – maintains information about various types of objects (inventory), events (transactions), people (employees), and places (warehouses)
Database models include:
1)Hierarchical database model – information is organized into a tree-like structure (using parent/child relationships) in such a way that it cannot have too many relationships.
2)Network database model – a flexible way of representing objects and their relationships.
3)Relational database model – stores information in the form of logically related two-dimensional tables.
Entity – a person, place, thing, transaction, or event about which information is stored
The rows in each table contain the entities
In Figure 7.1 CUSTOMER includes Dave’s Sub Shop and Pizza Palace entities
Attributes (fields, columns) – characteristics or properties of an entity class
The columns in each table contain the attributes
In Figure 7.1 attributes for CUSTOMER include Customer ID, Customer Name, Contact Name
Potential relational database for Coca-Cola

Primary keys and foreign keys identify the various entity classes (tables) in the database
Primary key – a field (or group of fields) that uniquely identifies a given entity in a table
Foreign key – a primary key of one table that appears an attribute in another table and acts to provide a logical relationship among the two tables
Database advantages from a business perspective include:
1)Increased flexibility
2)Increased scalability and performance
3)Reduced information redundancy
4)Increased information integrity (quality)
5)Increased information security
A well-designed database should:
1)Handle changes quickly and easily
2)Provide users with different views
3)Have only one physical view.Physical view – deals with the physical storage of information on a storage device
4)Have multiple logical views
5)Logical view – focuses on how users logically access information
A database must scale to meet increased demand, while maintaining acceptable performance levels
Scalability – refers to how well a system can adapt to increased demands
Performance – measures how quickly a system performs a certain process or transaction
Databases reduce information redundancy
Redundancy – the duplication of information or storing the same information in multiple places
Inconsistency is one of the primary problems with redundant information
information integrity measures the quality of information.
integrity constraint is the rules that help ensure the quality of information.
1)Relational integrity constraint
2)Business-critical integrity constraint
Information is the organizational asset and must be protected.
There have several databases security features:
1) Password : provides authentication of the user
2) Access level : determines who has access to the different types of information.
3) Access control : determines types of user access,such as read-only access,
Database management systems (DBMS) – software through which users and application programs interact with a database

Data-driven Web sites – an interactive Web site kept constantly updated and relevant to the needs of its customers through the use of a database

Data-driven web site business advantages :
1)Development
2)Content management
3)Future expandability
4)Minimizing human error
5)Cutting production and update costs
6)More efficient
7)Improved stability
Data driven business intelligence:
BI in data-driven web site

Integrating information among multiple databases:
Integration- allows separate systems to communicate directly with each other.
1) Forward integration : takes information entered into a given system and sends it automatically to all downstream systems and processes.
2) Backward integration- takes information entered into a given system and sends it automatically to all upstream systems and processes.
Forward integration:

Backward integration:

Building a central repository specifically for integrated information

Posted by Unknown at 20:21 0 comments